
Before you start building your ecommerce website, there are some important steps and practical challenges that you might not hear about. Being aware of these can help you prepare better and make the process smoother. To avoid common mistakes, you need to take the time to plan properly. As a full-service software development company in Kochi, we’ve seen real risks and steps that no one tells you about. Here is a clear, practical guide that tells you what to do, what could go wrong, and how to reduce the risk.
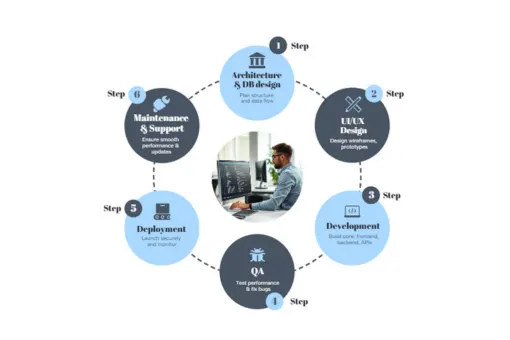
Step 1: Understand What You Really Need
Before we write a single line of code, our first step is to deeply understand your business Through an intake workshop, we listen like a story of your business, your products, customers, and fulfilment model, to determine whether the need is selling their own products/brands directly to the customer like (D2C) direct to customers or a marketplace of selling third party sellers, or a hybrid model. So we have to plan it accordingly.
After that, we map your primary user journeys from browsing to returns (browse → cart → checkout → fulfilment → returns) and convert this into a succinct Business Requirements Document (BRD). Risks include misinterpreting the model (you build D2C flows, but the client needs marketplace onboarding) and failing to notice hidden requirements (tax laws, COD regulations, and multi-vendor commissions) when you hand it off to an inexperienced partner. We incorporate this understanding into a scoped Statement of Work (SOW) and demand approval of the BRD prior to the start of any design or development to guarantee alignment.
Step 2: Choosing your ecommerce development Partner
Step 3: Choosing the best service partner
Your eCommerce success depends on your choice of service partners. Every decision affects performance, dependability, and customer experience, from payment gateways and shipping companies to hosting, messaging, and alerting systems.
1. Choosing a payment gateway
Picking the right payment gateway is very important because it is the engine of your eCommerce revenue and has a direct effect on cash flow, customer trust, and overhead. If you make a bad choice, you could lose sales.
Payment Methods: It must support how your customers pay. For India, this means UPI (like PhonePe), digital wallets, and Buy Now, Pay Later (like Simpl). If you sell abroad, ensure it accepts international credit cards. Understand the transaction fees (e.g., 2% + ₹3 per order) and how often you get your money (settlement frequency—daily or weekly). Also, check their rules for handling customer disputes and refunds.
Look for a gateway with clear documentation and tools that make it straightforward for developers to connect to your website or app. Consider Trusted Providers like Razorpay (great for Indian businesses), Stripe (favored by developers for global sales), and PayPal (widely recognized). Compare their fees and features to find the best fit.
2. Choosing shipping & logistics partners
Selecting the right shipping partners is crucial for maintaining profitability and customer satisfaction. Your choice directly affects delivery speed, operational costs, and how smoothly you handle returns. Focus on three key areas. Service coverage – do they deliver to all your customer pin codes, and what are their guaranteed delivery timelines (SLA)?, pricing model (cost per weight or zone), pickup scheduling process, and Proof of Delivery (POD) system, strong technical integration via APIs for automatic rate calculation, tracking, and manifest generation.
The practical risks are significant. High shipping costs to remote areas can erode your margins, while carriers that don’t offer pickup services create major operational hurdles for small merchants. Begin with 1-2 core carriers and expand once you have real cost data. Integrate smart shipping rules at checkout, like free shipping thresholds, to control costs automatically. Finally, build automated return workflows to process requests, generate labels, and update inventory, which minimizes human error and operational strain.
3. Push notification & messaging providers
You typically have three options: Mobile Push (sent to phones via apps), Web Push (sent to browsers), and In-App Messages (displayed only within your application). Providers like Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM), OneSignal, and AWS SNS facilitate these communications. A critical consideration is opt-in policy and GDPR/consent handling, as sending marketing messages without explicit user permission violates regulations and damages trust.
Sending too many notifications leads people to unsubscribe. To reduce these risks, focus on value-driven communication. Implement event-based notifications that users want to receive, such as order status updates or abandoned cart reminders. Always use frequency caps to avoid overwhelming your audience. Finally, test all notifications across Android, iOS, and web to ensure they display correctly and work as expected.
4. Choosing Your Email, SMS, and WhatsApp Providers
Your choice of communication providers is vital for ensuring your messages reach customers reliably and legally. Maintaining a clear separation between transactional messages (like order confirmations) and promotional campaigns is essential, especially considering regional SMS regulations, which vary significantly by country. However, in some regions, SMS costs are higher, especially for promotional traffic. In these markets, WhatsApp Business API has become a more affordable and engaging alternative for customer communication. Businesses use it for order updates, shipping alerts, and marketing messages, often achieving better open and response rates than SMS or email. Common providers include SendGrid and Amazon SES for email, and Twilio or local SMS aggregators for text messages.
A wrong configuration can cause major issues. Your emails may land in spam, and SMS campaigns can fail due to unregistered templates or DND restrictions. To avoid this, configure DKIM, SPF, and DMARC for better deliverability, use separate domains for transactional and marketing emails, and follow local SMS regulations with a clear opt-in process to stay compliant and trusted.
5. Choosing Your Hosting / Deployment Partner
Your hosting choice directly affects your website’s cost, performance, and security. Pick a reliable cloud provider such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure, and decide whether you want managed hosting (easier to maintain but comes at a premium) or self-managed hosting (more affordable but requires technical expertise).
A good setup should also include a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to cache and deliver your site’s content from multiple global servers, reducing latency and ensuring faster load times for users everywhere.
Make sure your hosting environment supports automated backups, disaster recovery, autoscaling to handle traffic surges, and robust security measures like HTTPS encryption and a Web Application Firewall (WAF) to protect against cyber threats.
Step 3: Testing & Quality Assurance (QA)
After product entry, the eCommerce website goes through a rigorous testing phase to ensure everything works perfectly before launch. At Fegno, testing is done in three layers, UAT (User Acceptance Testing), Alpha, and Beta, each designed to identify issues at different stages.
The project first moves from the development environment to a staging environment, where the system is tested in conditions close to live usage. Once verified, it is deployed to the production (live) environment, followed by final checks to ensure real-world stability, speed, and security.
During this stage, we validate user experience, functionality, payment flow, and responsiveness across all devices. Every bug or performance issue is logged, fixed, and retested, ensuring your eCommerce platform runs smoothly before it reaches customers.
Step 4: Product Entry / Vendor Onboarding
Product entry is one of the most time-consuming yet vital steps in launching an eCommerce store. Each product must be added with meticulous detail and a logical, hierarchical structure: Main Category → Subcategory → Brand → Specific Attributes.
These attributes such as color, size, material, and technical specifications are what make your site’s search and filter functions work effectively. For example, a customer looking for a headset should be able to filter by category (Electronics > Audio), type (Over-ear, On-ear), and features (Active Noise Cancellation, Boom Mic). The more detailed your attributes, the easier it is for customers to find exactly what they need.
Accuracy is important here because it has a direct impact on both the user experience and the visibility of your website in search engines. To ensure a seamless launch, we strongly advise entering your products after the initial testing and deployment phase.
Step 5: Go Live - Launching Your eCommerce Website
Once the website passes all testing stages, it’s time to go live. This is where your eCommerce store moves from staging to the production environment, becoming accessible to real users. Before launch, our team performs final checks — from SSL verification and payment gateway testing to browser compatibility and speed optimization.
The goal is a smooth, zero-error launch that gives your customers a fast and secure shopping experience from day one.
Step 6: Order Fulfillment
Everything, including your website and back-end functions, connects here. From a single dashboard, our custom eCommerce platforms allow for seamless integration with your ERP system, allowing automated order tracking, stock management, email and SMS updates, and delivery partner coordination.
Platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce frequently require manual intervention or separate staff management, but this all-in-one integration does away with those needs. It ensures faster order processing, fewer errors, and a smoother experience.
Step 7: Marketing
Step 8. Software Maintenance & Optimization
After launch, your eCommerce platform enters a continuous improvement cycle — because success doesn’t stop at going live. Regular maintenance ensures your system stays secure, stable, and fast, giving customers a seamless experience every time they visit.
This ongoing process includes monitoring server uptime to prevent downtime, updating frameworks and plugins to stay compatible with the latest technologies, and patching security vulnerabilities before they become risks. It also involves analyzing user behavior and performance metrics to identify what’s working and what needs refinement — from page speed and navigation to checkout flow and mobile usability.
Consistent optimization not only enhances customer satisfaction and trust but also boosts search engine performance and conversion rates. In short, regular maintenance transforms your eCommerce site from a one-time project into a living, evolving digital asset that continues to grow your business.


 Schedule An Appointment
Schedule An Appointment